This site provides insights into the nature of the amino acids and how they substitute for each other. It is an update on a series of pages first developed in 1999 to aid geneticists who used to ask Rob a lot of questions about amino acids and what did it mean to change from one to another. Since then, the pages have remained the most accessed tools we've ever developed and the Book Chapter describing them has been cited more than 1000 times. We thought it was high time to update them. If you love the 1990s style old pages, you can still see them at aasold.russelllab.org.
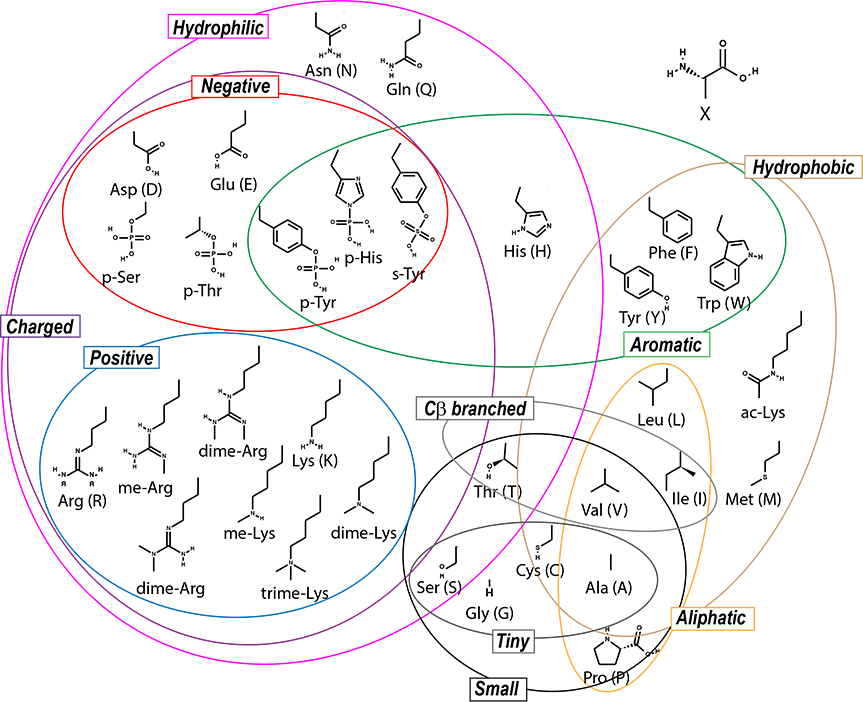
There are pages with information on each amino acid, in addition to others talking more generally about concepts. You can access these easily by using this clickable Venn diagram:

| Ala | Cys | Asp | Glu | Phe | Gly | His | Ile | Lys | Leu |
| Met | Asn | Pro | Gln | Arg | Ser | Thr | Val | Trp | Tyr |
| pSer | pThr | pTyr | pHis | sTyr | acLys | meLys | dimeLys | triemeLys | meArg | dimeArg | trimeArg |
| Hydrophobic | Aliphatic | Aromatic | Polar/Hydrophilic | Charged | Small | Tiny | C-beta branched | The main chain |
| Functional site tendencies |
| Evolutionary conservation |
| Substitution matrices |
| Some of our studies of genetic variants |
Citation:
M.J. Betts, R.B. Russell. Amino acid properties and consequences of subsitutions.
In Bioinformatics for Geneticists, M.R. Barnes, I.C. Gray eds, Wiley, 2003.
Author: Rob Russell, Heidelberg University